Dark Chocolate Ingredients: What's in It?
Use this search box to find the info you're looking for!

Pure dark chocolate ingredients are chocolate liquor, cocoa butter, cocoa powder and a sweetener. That's it. That's all there is in plain, pure dark chocolate.
But there can be other ingredients in chocolate and still meet the FDA's requirements.
Learn about each ingredient and what it contributes to the making of your favorite bittersweet treat.
Find out which dark chocolate ingredients are essential.
Interested in how dark chocolate is made? Watch this short video.
Cocoa Beans
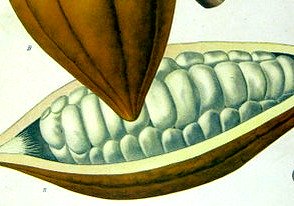 Cacao beans still in the pod.
Cacao beans still in the pod.It all starts with the chocolate tree, Theobroma cacao. Contrary to what the name implies, it produces pods containing cocoa beans not chocolate.
These precious beans are the source of that delicious chocolate taste you crave.
But it takes a lot of work to turn them into your favorite dark chocolate treat!
The first step is fermentation. It causes critical chemical changes in the beans needed to coax the chocolate flavor out.
The beans have a unique flavor (believe me, I've tried them) but don't taste like chocolate, yet.
So they must be roasted. Proper roasting brings out the flavor and aroma of the chocolate and reduces the bitterness.
Precise time and temperature control are crucial to get the desired taste.
Now that the beans are bursting with chocolate flavor it's time to remove the shells.
Set them free to become all they can be!
Cocoa Nibs
Break up the cocoa bean and remove the shell and your left with the nibs or flesh of the bean.
These nibs are about 50 to 60% cocoa butter.
These little nuggets can be eaten as is or added to candy or cookies, etc. They supply dark chocolate taste and a satisfying crunch.
But most nibs are ground. This causes the cocoa butter to melt producing liquid chocolate.
Chocolate Liquor
Chocolate liquor is nothing but liquid chocolate, tiny bits of cocoa suspended in cocoa butter.
It's thick, brown and contains no alcohol.
It's the dark chocolate ingredient that's the foundation for all chocolate products.
It's pure and can be sold as baking, bitter, or unsweetened chocolate.
Or processed into other real chocolate products like chips, candy or enrobing chocolate (used for coating).
Or the liquid chocolate can be pressed to extract the fat from it.
Cocoa Butter
 Cocoa butter pieces.
Cocoa butter pieces.The fat found in chocolate is cocoa butter and there's lots of it. Thankfully, it doesn't raise your cholesterol.
But it does provide the decadent richness and texture that's part of chocolate's appeal.
Ever wonder why chocolate melts on your tongue? It's because cocoa butter's melting point is just slightly lower than your body temperature.
The dark chocolate slowly melts away leaving no waxy aftertaste, just a smile.
Real chocolate has extra cocoa butter added to make it melt smoothly.
This critical chocolate butter is in great demand. It's one of the most expensive ingredients in chocolate.
But chocolate ain't chocolate without it.
Cocoa Powder
What's left after almost all the fat is squeezed out of the chocolate? A cake of cocoa. It's finely ground to make cocoa powder.
This dark chocolate ingredient is rich in antioxidants and very versatile.
It's used to increase the cacao (cocoa) content of chocolate products or as a substitute when baking.
Go to dark chocolate cocoa and learn why you need some in your life.
Just don't try to eat it right out of the can. It's w-a-a-a-y too bitter but it smells great!
Sweeteners
You can't enjoy your real dark chocolate without a sweetener. But FDA rules allow only nutritive carbohydrates to be used in standard of identity chocolate (real chocolate).
That means sweeteners that supply calories. Only sugar from sugar cane and sugar beets can be used.
No artificial sugar or substitutes are allowed.
Optional Dark Chocolate Ingredients
Milkfat, vanilla, and lecithin are the most common optional ingredients found in real dark chocolate.
Dark chocolate can be a little hard. So some manufacturers add milkfat. It's derived from dairy butter oil, the only other fat allowed in real chocolate in the U.S.
Milkfat is made from butter that has had almost all the moisture and nonfat solids removed.
It's used to add flavor, make the chocolate softer, and reduce the chance of fat bloom. Those ugly whitish fat crystals that can form on the chocolate but don't ruin it.
Vanilla is sometimes used to add flavor to the chocolate. Real vanilla is made from vanilla beans.
But artificial vanilla can be made from lignin (waste product of paper industry) or guaiacol (from the chemical industry).
Lecithin, usually derived from soybeans, is used as an emulsifier. It's added to help preserve the even distribution of the cocoa butter in the chocolate and make it flow easier.
These and other flavors can be used as long as they don't imitate the flavor of chocolate, milk or butter.
But when it comes to dark chocolate do we really need any other flavors?
Creating dark chocolate is a long, complex process. But it's those dark
chocolate ingredients, combining in an almost magical way, that make it
the greatest flavor on the planet. Each cocoa bean component is vital,
there's just no substitution for the real stuff!
Return to What is Dark Chocolate?
Return to Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate Home Page
New! Comments
Feeling the need to send some feedback? Leave me a comment in the box below.